NordDLO: Diffusion Limited Oxidation, Heterogenous Aging
Using an AI-driven continuum model, NordDLO is a three-dimensional kinetic solver that helps our customer to address their product design and development challenges for surface oxidation due to Diffusion limited Oxidation. The solver predicts oxidative degradation rates in combined thermal and radiation environments.
Our experimental analysis has shown most of the oxygen will be consumed on the surface layer of the material, especially at high temperatures, which creates a protective layer that prevents the core of the material from being affected by oxidation. This phenomenon is called Diffusion Limited Oxidation or short DLO. Our DLO model shows that polymers exposed to thermal aging at different temperatures can have different oxygen consumption levels as shown here. Higher temperature creates an oxidized surface, which acts as an insulation layer and reduces oxygen consumption. On the other hand, it results in crack formation and Chemical changes on the surface, which changes the mechanical performance of the polymer. Nord-DLO enables a large variety of Thermo-chemical and thermo-mechanical simulations of oxidation progress in polymers that incorporate the coupling between diffusion, chemical reaction, and large deformation of polymers.
Nord-DLO is an add-on extension that runs in parallel to either NordRad or NordPoly. While in most current aging software for oxidative aging simulation, diffusion-limited oxidation (DLO) effects are eliminated, DLO is particularly important in large-time domains and ultra-long aging events. Our DLO model provides unprecedented accuracy to long-term simulations where most current models that use accelerated aging and shift factors fail. NordDLO allows the measurement of degradation rates directly, and therefore rather, the effects of aging are often monitored under accelerated aging conditions, for example, as changes in mechanical properties such as tensile elongation. NordDLO is compatible with FEA solvers such as Abaqus, Ansys, and MOOSE.
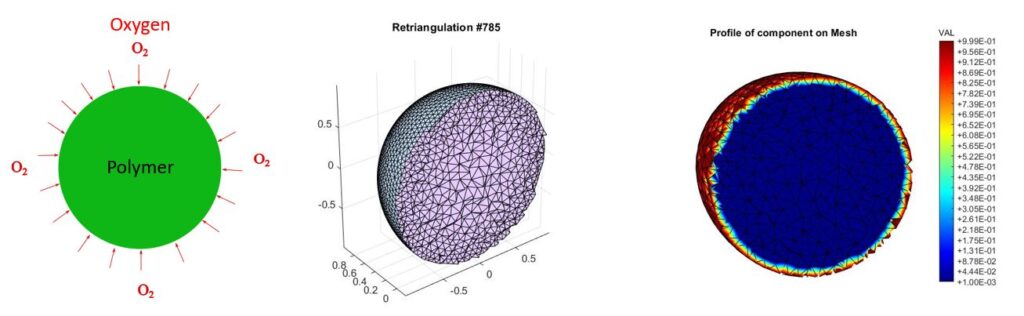
Below shows the schematic of the 3D problem of the DLO Effect in a polymer ball with external exposure to O2, the shape of the mesh, and profile of the O2 diffusion.